|
EasyOCR is a multi-font, printed, character reader
based on a template matching algorithm. In the learning phase, it is taught
a font by giving it samples of all possible characters. Then, it is able to
read any kind of short text. Blob analysis functions are used to segment
the image and extract the characters constituting the text to be read. Blobs
are elected as characters based on tunable size and shape criteria.
Moreover, EasyOCR is able to deal with characters
which are split into several blobs. When the exact position of the
characters in the image is unknown, EasyOCR
functions will process the entire image and locate the characters.
Recognition process
EasyOCR follows a few steps in the recognition
process.
First, the image is segmented, i.e. threshold and decomposed into
objects or blobs (connected components), in the
same way as EasyObject does.
Then the objects are filtered according to the size and possibly grouped
together ("repasted") to form distinct characters.
This is called character isolation or
segmentation. When several characters touch each
other, they can also be separated. This is called character
cutting. The segmentation step can be bypassed
when the exact position of the characters is known beforehand.
The characters are compared to a set of patterns,
called a font. A character is recognized by
finding the best match between a character and the patterns in the font.
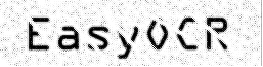
Raw image
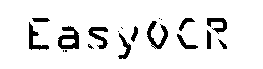
After segmentation
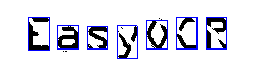
After character isolation

After recognition
The recognition process consists of the
following elements:
- Read a pre-recorded font from a disk
file;
- Segment the image to locate the
characters;
- Select the objects considered as
characters and sorts them from left to right;
- Perform the matching from object to
characters
Recognition parameters
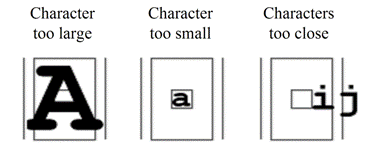
The recognition process is governed by a few parameters that need to be
fine tuned to obtain the most reliable results.
-
TextColor : black text on a white background, or conversely, with or without
thresholding;
-
Threshold value used to separate the text from the background. The threshold
value should be chosen such that the characters are well separated.
-
RemoveBorder: most of the time, blobs that are found along the image/ROI
edges are spurious and cannot be exploited for character recognition. By
default they are discarded for character isolation;
-
NoiseArea: if a blob has an area smaller than this value, it is
considered as noise and discarded. The NoiseArea should be chosen such that
the noise blobs are discarded but small character features are preserved
(f.i., the dot over an "i" letter);
-
MaxWidth,
MaxHeight: if a blob does not fit within a rectangle with these
dimensions, it is not considered as a possible character (too large) and is
discarded. Furthermore, if several blobs fit in a rectangle with these
dimensions, they are grouped together, forming a single character. The outer
rectangle size should be chosen such that it can contain the largest
character from the font, enlarged by a small safety margin;
-
MinWidth,
MinHeight: if a blob or a group of blobs does fit in a rectangle with
these dimensions, it is not considered as a possible character (too small)
and is discarded. The inner rectangle size should be chosen such that it is
contained in the smallest character from the font, shrunk by a small safety
margin;
-
RemoveNarrowOrFlat: by default, small characters are discarded when they
both narrow and flat. This behavior can be changed so that they are
discarded when either condition is met.
-
Spacing: if to blobs are separated by a vertical gap wider than this
value, they are considered to belong to different characters. This feature
is useful to avoid the grouping of thin characters that would fit in the
outer rectangle. Its value should be set to the width of the smallest gap
between adjacent letters. If it is set to a large value (larger than
MaxWidth), it has no effect.
-
CutLargeChars: when a blob or grouping of blobs is larger than the
maximum allowed width, it is considered as clutter and discarded. When the
CutLargeChars mode is enabled, the blob is split in as many parts as
necessary to fit. This is an attempt to separate touching characters;
-
RelativeSpacing: when the CutLargeChars mode is enabled, setting this
value allows specifying the amount of white space that should be inserted
between the split parts of the blobs;
Learning
EasyOCR is a multi-font character recognition
library. This means that EasyOCR functions are
able to recognize text printed using any character font, once it has been
taught. Practically, during the learning process, characters are presented
one by one to the system which analyzes them and builds a database called a
font.
Only a few data are stored for each new character, they represent
distinctive features of the character’s shape. This small database may be
saved to disk and restored when needed.
During the learning process, each pattern gets an associated numerical
value call its code (usually its ASCII code). A
pattern also belongs to a character class.
|