|
The TextureMatcher finds the nearest matching texture among a set of
reference images. The distance measure is based on frequency information in
two directions.
A texture is given a name. To each texture multiple reference images is
associated to improve matching performance.
The tool is suitable for the following applications:
- Surface Classification
- Object Identification
Typical task for texture matching is matching images like:
 
Texture Matching is used and very powerful when it is impossible to
extract physical features from the image.
Basic principle for Texture Matching
on 8bit grey-scale images
The image is converted to three image by applying a low - medium - highpass
filter along every line in x-direction.The same filter is applied to the
three resulting images in the y-direction. The nine resulting images are
used to produce the nine coefficients:
LxLy LxMy LxHy
MxLy MxMy MxHy
HxLy HxMy HxHy
The LxLy represents to low frequency content in x and y direction. HxLy
contains the high frequency content in x and the low frequency content in y
and so on.
For each image there is generated a mean value and a standard deviation for
each coefficient. Experience has shown that removing LxLy which includes the
DC component of the image can be advantages.
The eight dimensional vector of mean values describes a two dimensional
frequency content of the image / reference. The standard deviation is
describes the uncertainty in the coeefisient estimation and is used a
weight in the distance measure comparing and image and its reference.
The distance is in general described:
sum of all abs ( RefNxNx - NxNx ) / ( RefStdev )
One can see that the coefficients with low standard deviation is weighted up
and that the weight are from each reference. The standard classification is
to select the reference with the smallest distance.
The distance calculation is not time consuming. This means that limited the
number of references does not save anything. Adding reference will normally
lead to better sorting because the class description is better the more
references.
References
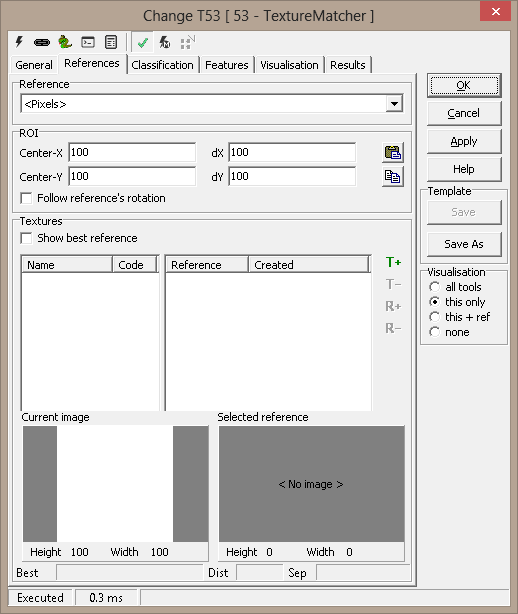
Reference - Reference system selection
ROI - the tool's region of interest
- Center-x - center x of the ROI
- Center-y - center y of the ROI
- dX, dY - Width and
height of the search area
Point & Click Clipboard Support
 The rectangular
ROI is defined by four points. The rectangular
ROI is defined by four points.
One point will change the center point.
More on Image Operations.
Textures
- Show best reference - You can choose to show the best reference to a
texture image. It is updated while running the inspection in the
Selected reference image pane.
 - Adds
texture with a given name - Adds
texture with a given name -
Removes a texture including all reference images -
Removes a texture including all reference images - Adds
a reference to the selected texture - see also "Adding references using
Point & click" - Adds
a reference to the selected texture - see also "Adding references using
Point & click" -
Removes the selected reference -
Removes the selected reference- Current Image - Image is updated when an inspection is
performed - the image region is transferred from the captured image
- Selected Reference - displays the image of the best or selected
reference
- Status bar
- Best - name of color
- Dist - Distance of best match
- Sep - logarithmic separation between best texture and second best
texture
Reference Mouse Menu The following
items are available in the reference list mouse menu:
-
Add Reference
-
Delete Reference
-
Rename Reference
-
Delete All References
Adding references using Point & Click

By adding a point to the clipboard selecting the a named
texture pressing  will add a reference image to the tool - a rectangle defined by four points
is also supported.
will add a reference image to the tool - a rectangle defined by four points
is also supported.
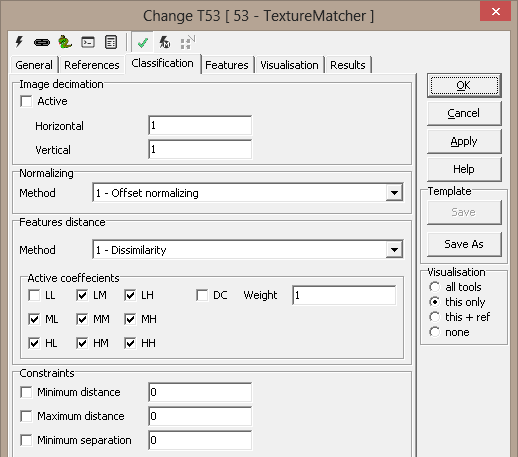
Classification
Image decimation
Note - Image decimation speeds up the
TextureMatcher - it is by default off
Normalizing - used to make the texture matcher less sensitive to
intensity variations
-
Method
-
1-Offset - default
-
2-Offset and mean-gain
-
3-Offset and std-gain
Features distance - specifies how to calculate
the distance - difference is the best method
-
Method
-
Active coefficients
Constraints - to specify an absolute criteria to
accept a texture
Features
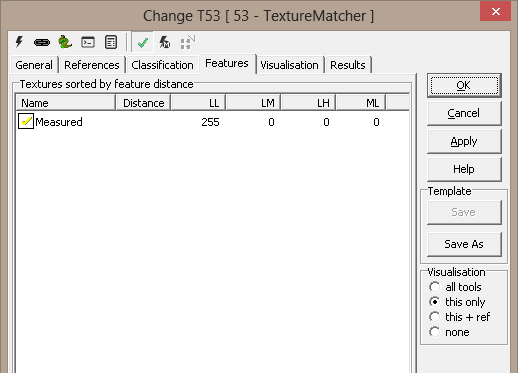
Textures sorted by feature distance - The textures are here sorted
after feature distance, thus you can see the best match. Reference not
meeting the constraints are display with a yellow checkmark.
Visualisation
|
Center
|
Center position of ROI
|
|
ROI
|
Region of interest
|
Results
|
Match
|
True if a
color is matched - meeting the constraints requirement |
|
Texture
|
Name of matched texture
|
|
Reference
|
Name of matching reference
|
|
Distance
|
Distance between image and best reference
|
|
Separation
|
The logarithmic separation between matched texture and the second best texture
|
|
Coefficients
|
Values for the active coefficients
|
|
Weights
|
Values for the weights
|
|
Texture[]
|
Matching sequence
|
|
Distance[]
|
Distance for each texture to current image
|
ExecuteCmd support - more
information
|
Command
|
Parameters
|
Return values
|
Comments
|
|
Set |
Object=ROI;Value=<polygon>
Object=ROI;Value=cx,cy,dx,dy |
ok,res
ok,res |
Sets the tool's ROI. See Copy/paste
ROIs for details. |
|
Get |
Object=ROI |
ok,<polygon> |
Current ROI as rectangular, closed polygon |
| Set |
Object=Reference;Texture=<texture>;
[
Name=<name>;][Code=<code>;]
Value=<polygon>
|
ok,None
|
Creates
or replaces named texture reference. The polygon defines the reference's
position in the image. Name and Code are optional |
| Get |
Object=Texturenames |
ok,<names> |
All
texture names as a Python tuple |
| Get |
Object=Referencenames;Texture=<texture> |
ok,<names> |
All
reference names defined for the named texture |
| Delete |
Object=Texture;Name=<name> |
ok,None |
Removes
named texture and all its references |
| Delete |
Object=Reference;Texture=<texture>;
Name=<name> |
ok,None |
Deletes
specified texture reference |
| DeleteAll |
Object=Texture;Texture=<texture>; |
ok,None |
Deletes specified texture references |
| DeleteAll |
- |
ok,None |
Deletes
all textures and references |
Example 1 : TextureMatcher Classification
# read the results from the texturemacther
type = GetValue('TextureMatcher.Texture')
print type
match = GetValue('TextureMatcher.Match')
print match
#classifies a set of LogicTool based on the result
SetValue('Smooth.Value',type=='Smooth')
SetValue('Tree.Value',type=='Tree')
SetValue('Structure.Value',type=='Structure')
SetValue('Pattern.Value',type=='Pattern')
SetValue('Backside.Value',type=='Backside')
|