|
The ColorMatcher
is defined to find the closest color to an area of a color image. The user
can define Colors and a set of reference images to each Color. It is easy to
verify the color of e.g. a wire with the matcher.
 The ColorMatcher works this way:
For any reference the mean value of the Hue, Sat and
Intensity is computed. The mean value is the mean value across all pixels
within the ROI (Region of Interest).
When a sample color is tested in the tool, this happens:
-
The mean value of the Hue, Sat and Intensity is computed.
-
The Feature Distance is computed - see classification
section
-
The list of colors sorted on D values is then
produced.
-
The prefilter is now brought into play. For a
color with equal I but H and S values swapped the D will be the
same.
But the H and S values may differ. By placing a prefilter
constraint on say the H value the color with a greater H value than the
constraint will be marked yellow and will not contribute in the process.
-
The Max distance constraint will bring out of play any
colors with a D value grater than this constraint.
-
The Min separation constraint removes any matches with a
Separation lower than this value.
ReferencesReference - Reference system selection
ROI - the tool's region of interest
The ROI is managed by the buttons
- Paste - paste the ROI from the image to the scorpion clipboard
- Copy - copy the ROI to the image from the scorpion clipboard
Point & Click Clipboard Support
 The rectangular ROI is defined by four points.
The rectangular ROI is defined by four points.
One point will change the center point.
Colors
- Show best reference - when active the best reference is selected
for each inspection
- Current Image - Image is updated when an inspection is
performed - the image region is transferred from the captured image
- Selected Reference - displays the image of the best or selected
reference
- Status bar
- Best - Name of color
- Dist - Distance of best match
- Sep - Logarithmic separation between best color and second best color
 - Adds a color with a given name - Adds a color with a given name - Removes a color with it's
reference images - Removes a color with it's
reference images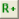 - Adds the current image as a
reference to the selected reference - Adds the current image as a
reference to the selected reference
 - Removes the selected reference - Removes the selected reference
Reference Mouse Menu The following
items are available in the reference list mouse menu:
-
Add Reference
-
Delete Reference
-
Rename Reference
-
Delete All References
Adding references using Point & Click

By adding a point to the clipboard selecting the a named
color and pressing  will add a reference image to the tool - a rectangle defined by four points
is also supported.
will add a reference image to the tool - a rectangle defined by four points
is also supported.
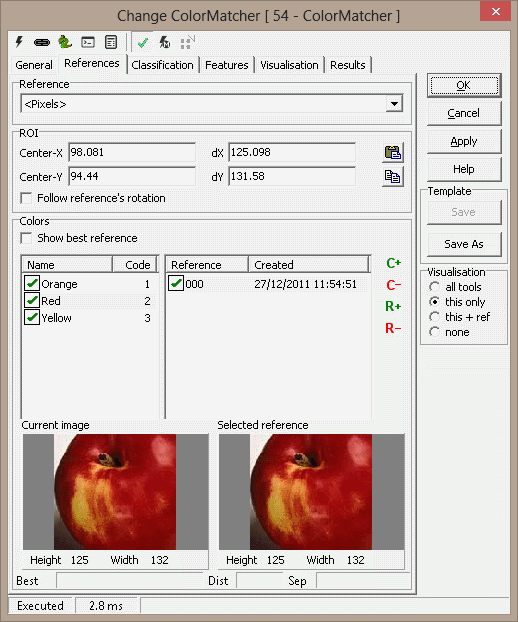
Classification Prefilter
Specifies the maximum deviation of the HSI from a
reference image - these filters are normally off. Can be used to tell
the tool that there is no or little intensity variations.
-
H - max deviation
-
S - max deviation
-
I - max deviation
-
H std - max deviation
-
S std - max deviation
-
I std - max deviation
Feature distance
Constraints
-
Maximum distance - the maximum distance between
the current image for a reference image to be accepted
-
Minimum Separation - the minimum separation between
the best and the second best color for the color to be accepted
Note : when a color isn't accepted the match result
is 0 or FALSE
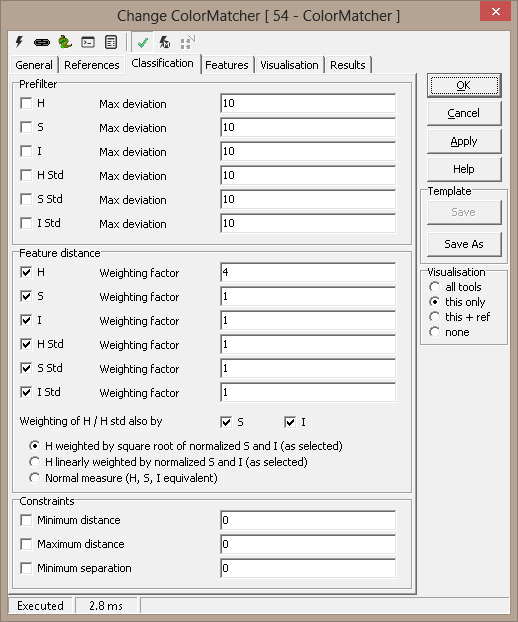
Features The feature list display a sorted, by
distance, list of reference images. The accepted reference are checked with
a green arrow.
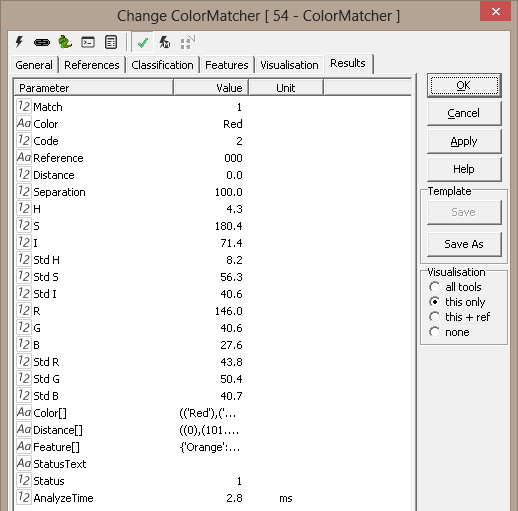
Results
|
Match
|
True if a
color is matched
|
|
Color
|
Name of matched color
|
|
Code |
The user defined index of the color |
|
Reference
|
Name of matching reference
|
|
Distance
|
Distance between image and best reference
|
|
Separation
|
Distance between matched color and the second closest color
|
|
HSI
|
Values for Hue, Saturation and Intensity
|
|
Color[]
|
List of defined colors |
|
Distance[]
|
Distance for each color to current image
|
|
Feature[] |
Complete feature list for reference images |
Visualisation
|
Center
|
Center position of ROI
|
|
ROI
|
Region of Interest
|
ExecuteCmd support (see also executeCmd)
|
Command
|
Parameters
|
Return values
|
Comments
|
|
Set |
Object=ROI;Value=<polygon>
Object=ROI;Value=cx,cy,dx,dy |
ok,res
ok,res |
Sets the tool's ROI. See Copy/paste
ROIs for details. |
|
Get |
Object=ROI |
ok,<polygon> |
Current ROI as rectangular, closed polygon |
| Set |
Object=Reference;Color=<color>;
[Name=<name>;][Code=<code>;]
Value=<polygon>
|
ok,None
|
Creates
or replaces named color reference. The polygon defines the reference's
position in the image. Name and Code are optional |
| Get |
Object=Colornames |
ok,<names> |
All
color names as a Python tuple |
| Get |
Object=Referencenames;Color=<color> |
ok,<names> |
All
reference names defined for the named color |
| Delete |
Object=Color;Name=<name> |
ok,None |
Removes
named color and all its references |
| Delete |
Object=Reference;Color=<color>;
Name=<name> |
ok,None |
Deletes
specified color reference |
| DeleteAll |
Object=Color;Color=<color>; |
ok,None |
Deletes specified color references |
| DeleteAll |
- |
ok,None |
Deletes
all colors and references |
Example 1:
features = eval(GetValue('ColorMatcher.Feature[]')) # a python
dictionary is generated
print features
#provides the following console output
{'blue': {'1': (137.83000000000001, 232.78, 52.390000000000001), '0':
(118.36, 115.31999999999999, 81.519999999999996), '3': (121.0, 131.84,
71.079999999999998), '2': (146.91999999999999, 255.0, 71.219999999999999),
'5': (118.68000000000001, 140.12, 71.239999999999995), '4': (126.0,
165.19999999999999, 71.359999999999999), '7': (102.04000000000001,
82.680000000000007, 81.680000000000007), '6': (60.799999999999997,
71.439999999999998, 95.560000000000002),
'green': {'1': (86.920000000000002, 43.219999999999999, 102.61), '0':
(51.399999999999999, 97.439999999999998, 94.200000000000003), '3':
(51.159999999999997, 85.319999999999993, 99.319999999999993), '2':
(53.880000000000003, 109.40000000000001,85.439999999999998),
'black': {'1': (143.0, 22.640000000000001, 51.969999999999999), '0':
(43.920000000000002, 68.879999999999995, 35.399999999999999),
'tree': {'1': (32.479999999999997, 63.159999999999997, 131.63999
999999999), '0': (33.079999999999998, 85.879999999999995, 119.88), '3':
(31.84, 98.519999999999996, 118.48), '2': (31.48, 76.239999999999995,
126.04000000000001),
'red': {'1': (9.4000000000000004, 114.16, 100.08), '0': (9.5999999999999996,
213.56, 74.090000000000003), '3': (10.56, 101.52, 106.40000000000001), '2':
(14.68, 75.120000000000005, 119.72)}}
Note : this result is provided to enable creation of custom
feature distance in python
Example 2:
colors = eval(GetValue('ColorMatcher.Color[]')) # generates a
python list
print colors
#provides the following console output
('tree', 'black', 'blue', 'green', 'red')
Example 3:
distances = eval(GetValue('ColorMatcher.Distance[]')) # generates a
python list
print distances
# the features distance corresponds to the color of the corresponding
element in the Color[] result
#provides the following console output
(46.299623839928799, 50.171249162203203, 54.0035532623723,
61.197111299248, 62.209603052612501)
Example 4:
It is possible
to define classification logic using a python script.
The following script example shows how to classify based on hsi values from
a Color Matcher:
h = GetValue('cm.H')
s = GetValue('cm.S')
i = GetValue('cm.I')
print 'hsi - ',h,s,i
red = ( 158 < h < 168 ) and ( s > 200 ) and ( 50 < i < 100 )
SetValue('Red.Value',red)
blue = ( 0 < h < 15 ) and ( 75 < s < 225 ) and ( 80 < i < 200 )
SetValue('Blue.Value',blue)
darkgrey = ( 118 < h < 150 ) and ( 0 < s < 75 ) and ( 60 < i < 120 )
SetValue('DarkGrey.Value',darkgrey)
Black = ( 0 < s < 40) and ( 0 < i < 60 )
SetValue('Black.Value',Black)
WhiteYellow = ( 127 < h < 137 ) and ( 100 < s < 200 ) and ( 120 < i < 180 )
SetValue('White_Yellow.Value',WhiteYellow)
brown = ( 138 < h < 154 ) and ( 50 < s < 150 ) and ( 80 < i < 120 )
SetValue('Brown.Value',brown)
|