The ImageCombiner tool is a flexible tool for image manipulation. The
following features are supported:
- Image Subtraction using static reference images
- Image Subtraction using running average of image
The tool has a reference and works within a Region
of Interest - ROI.
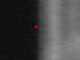
A typical application for Image Combiner is print verification. Below a
label is shown.

With Image Substraction a typical output image is shown below:

This image is normally analysed using a Blob tool. We see that the last
digit of the label sequence number is changing from label to label. The rest
of the label is more or less unchanged.
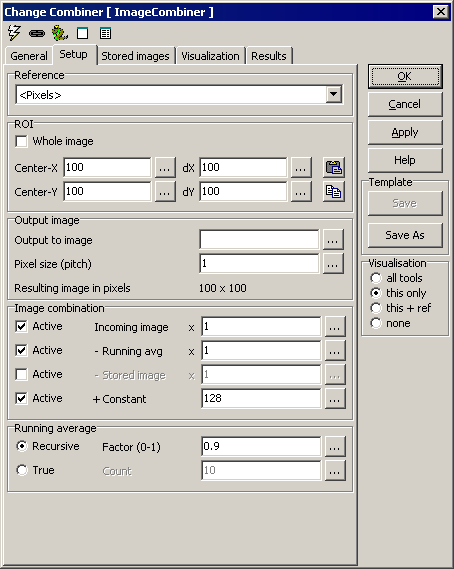
Setup
Reference - Reference system selection
ROI - image for calculation and ROI (region of interest)
- Whole image - ignore ROI settings and use all of the image
-
Center-X - x
- Center-Y - y
- dX - height
- dY - width
The ROI is managed by the buttons
- Paste - paste the ROI from the image to the scorpion clipboard
- Copy - copy the ROI to the image from the scorpion clipboard
Point & Click Clipboard Support
 The rectangular
ROI is defined by four points. The rectangular
ROI is defined by four points.
One point will change the center point.
More on Image Operations.
Output Image
- Output to image - name of image to present result
- Pixel size (pitch) - correspondence between input reference
units and output image pixels. A value of 1 means one output pixel per
input unit, 2 means one output pixel per two input units.
- Resulting image in pixels - the actual image size is shown
Image combination
The resulting image is made as a combination of the following:
- Incoming image - current image, possibly scaled by a factor
- Running avg - minus running average (see below),
possibly scaled
- Stored image - minus the mean value of all stored images
(see below)
- Constant - plus a constant
Running average
Two algorithms are available for calculation of the running average:
- Recursive: This is sometimes also called an exponential filter, or
infinite impulse response (IIR).
- True: The running average is calculated from the count last
incoming pictures.
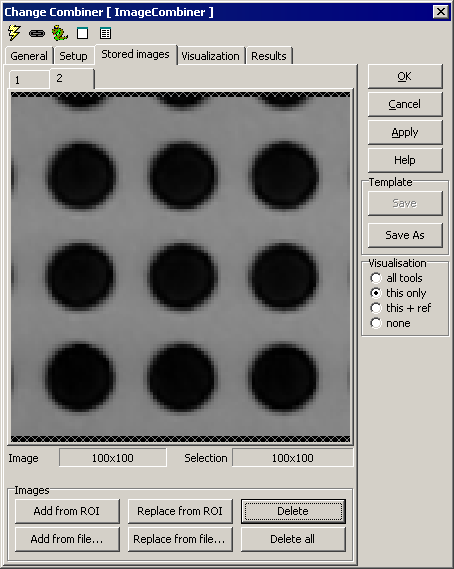
Stored Images
Any number of static images can be stored within the tool. When stored
image is selected for the calculation, a simple mean of all the stored
pictures is used and subtracted from the incoming image.
Note: All stored pictures must be of the same size, and also the
same size as the output image (in pixels). If any other pictures are stored,
the mean value will not be calculated or used. You are warned if different
size images are stored.
- Add from ROI - add the last input image to the store
- Replace from ROI - replace the visible stored image with the last
input image
- Add from file... - add an image read from file
- Replace from file... - replace the visible stored image with an
image read from file
- Delete - delete the visible image
- Delete all - remove all stored images
Visualisation
Results
|
Mean pixel ratio |
Mean pixel-to-pixel ratio between original and resampled picture.
Values larger than 1 means loss of information (decimation). |
ExecuteCmd support (see also executeCmd)
|
Command
|
Parameters
|
Return values
|
Comments
|
|
Set |
Object=ROI;Value=<point/polygon>
Object=ROI;Value=cx,cy,dx,dy |
ok,res
ok,res |
Sets the tool's ROI. See Copy/paste
ROIs for details. |
|
Get |
Object=ROI |
ok,<polygon> |
Current ROI as rectangular, closed polygon |
|
AddImage
|
-
|
ok,res |
Adds last incoming picture to store
|
|
ClearAll
|
-
|
ok,res |
Removes all pictures from store
|
|
DeleteImage |
Index=<n> |
ok,res |
Delete specified image from store; shift remaining images down in
index |
|
ReplaceImage |
Index=<n> |
ok,res |
Replace specified image in store by last incoming image |
Example1: # AddImage tool = GetTool('Combiner') #Get a handle to an ImageCombiner tool
tool.executeCmd('AddImage','')
Example2: # DeleteImage tool = GetTool('Combiner') #Get a handle to an ImageCombiner tool
tool.executeCmd('DeleteImage','Index=1')
|